Red Dragon – Red China – Hegemonist

Hegemony refers to dominance of one nation over others. Hegemonism is the policy or practice of a nation in aggressively expanding its influence over other countries.

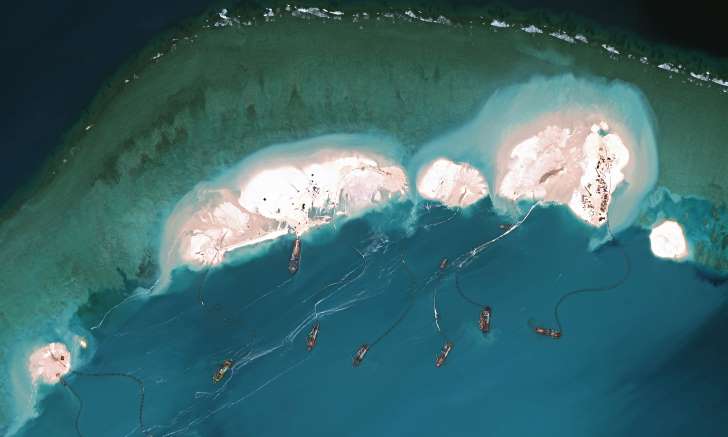
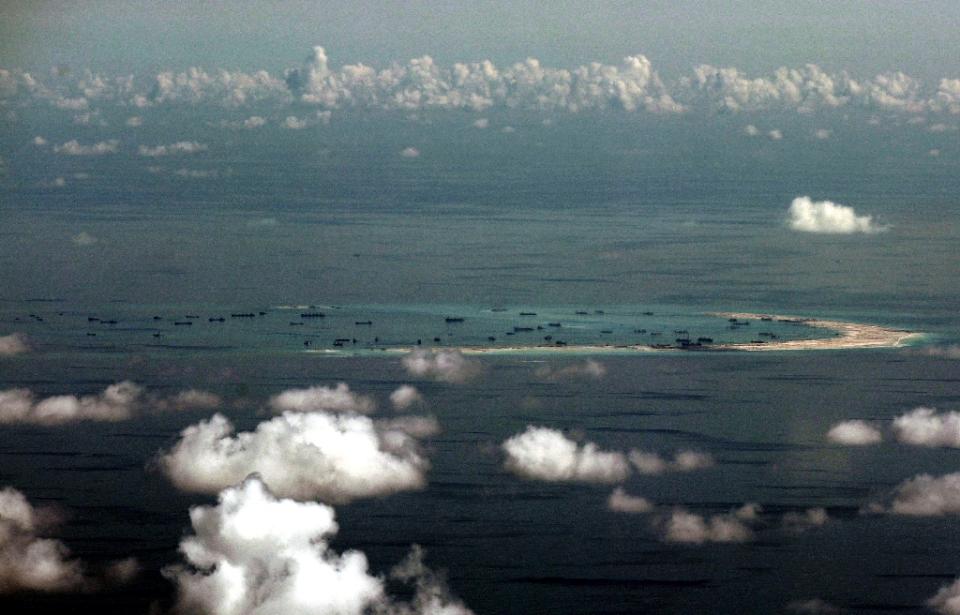
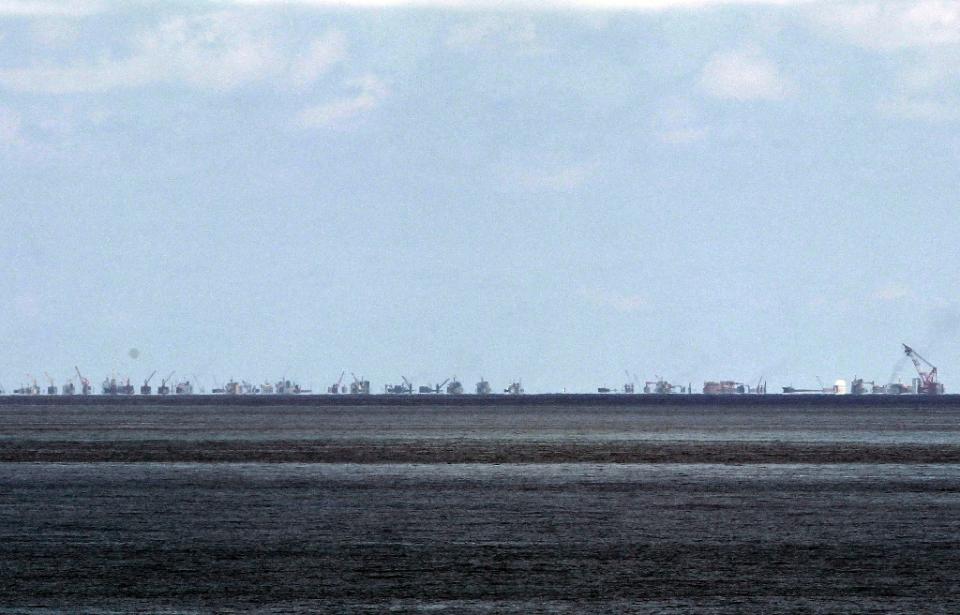
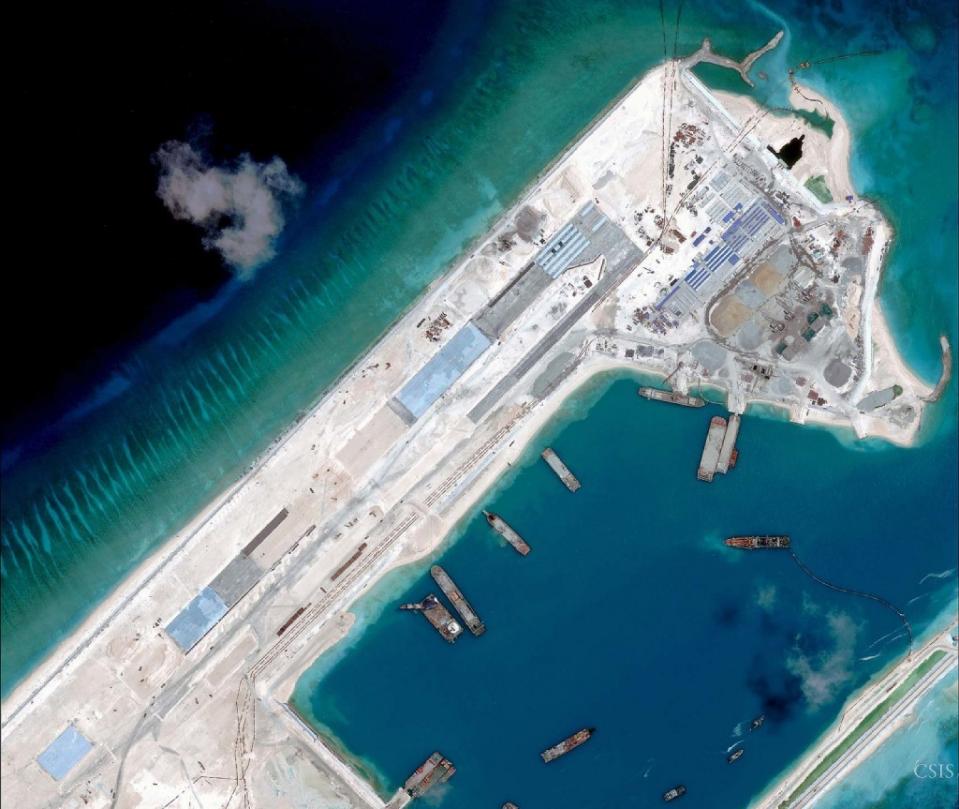
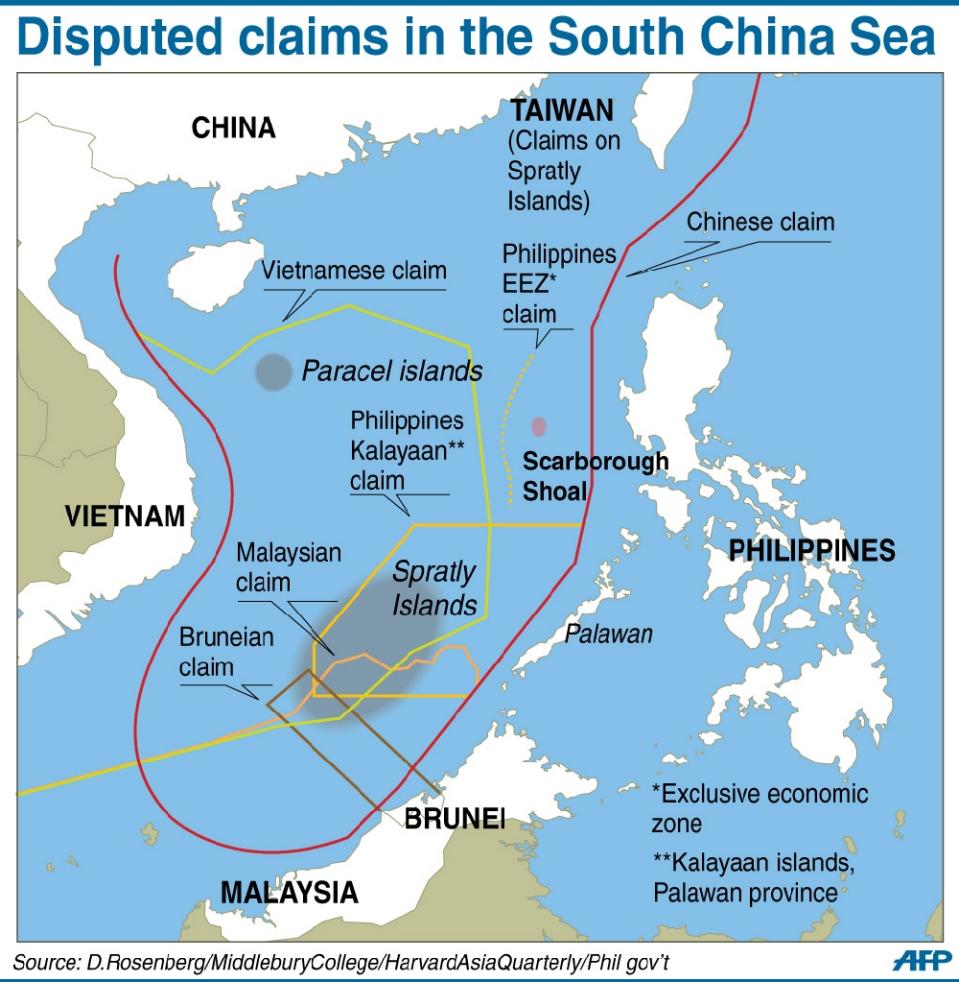
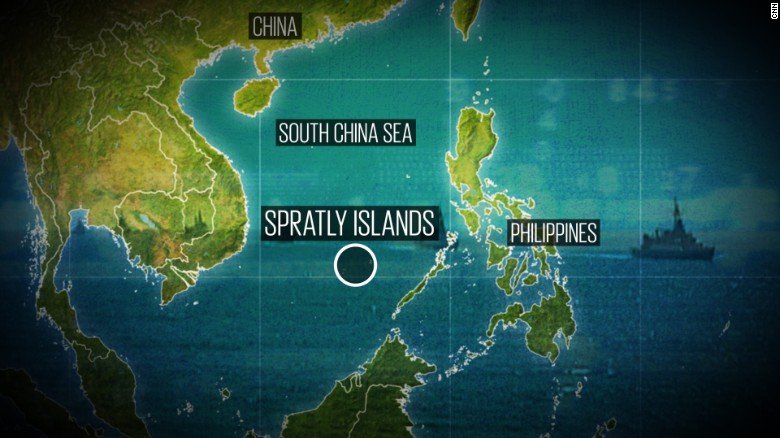
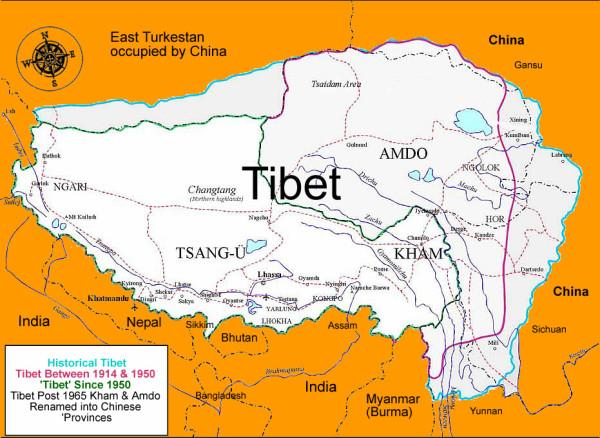
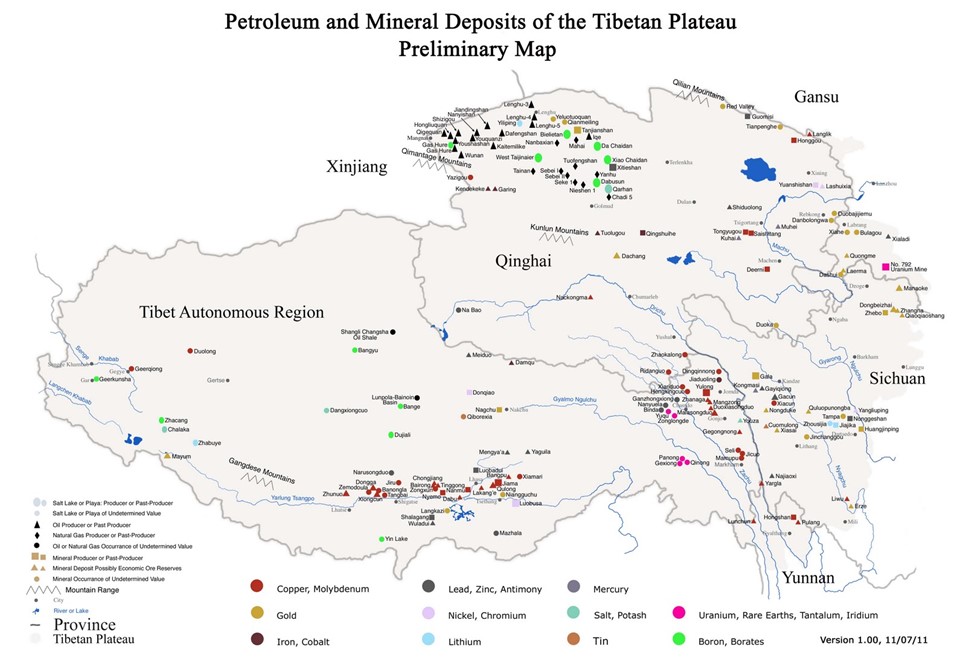
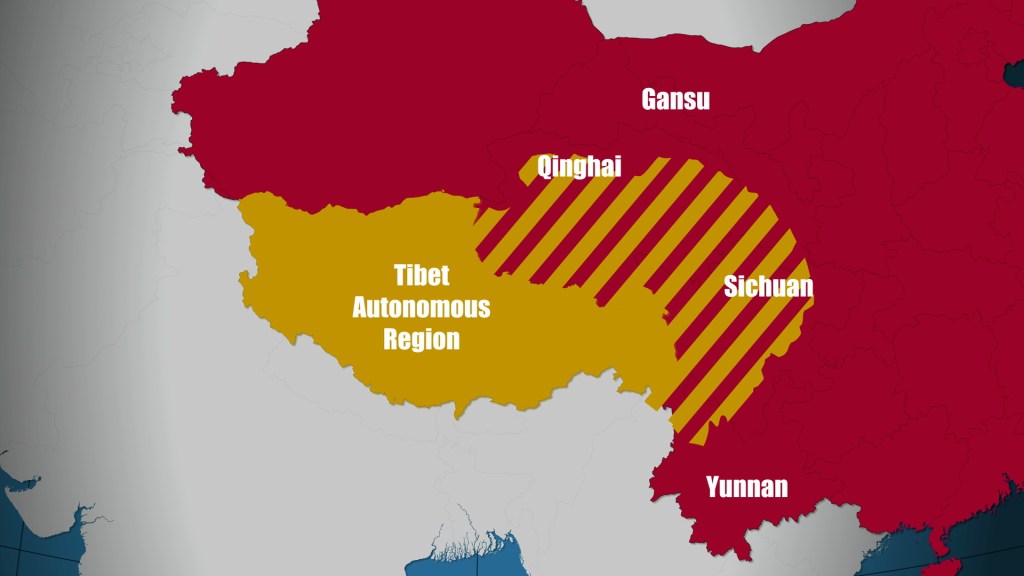
Red China heralded her hegemonistic policy in 1949 when she announced to the world that she would use military force to occupy Tibet which declared full independence on February 13, 1913. In October 1950, Red China attacked Tibet overcoming weak Tibetan resistance and occupied 965, 000 square miles of Tibetan territory which now represents one quarter of Red China’s landmass. This Tibetan territory includes entire Tibet Autonomous Region (TAR) and regions found in Qinghai, Gansu, Sichuan and Yunnan provinces. Red China’s policy of Hegemonism is nothing new. Red China will prevail with her military aggression in South China Sea if Red China is not evicted from Tibet.
I submit that we need not always Fight a War to Win a War. At Special Frontier Force, I am known as ‘Doomsayer of Doom Dooma’. I am claiming that we will Win our War against Tibet’s military occupation without fighting a War with Red China for I predict ‘Beijing Is Doomed’ and Red China set herself on irreversible path of Self-Destruction.

Rudra Narasimham Rebbapragada
Ann Arbor, MI 48104-4162, USA
Special Frontier Force-Establishment 22-Vikas Regiment

ValueWalk.
Game Theory: A New Twist To The South China Sea
Posted By: BRINDA BANERJEE Posted date: August 20, 2015 03:15:04 PM
If you haven’t heard of “HEGEMON” and you’re a geostrategy enthusiast, you’re missing out on a very interesting experience. Developed by the Potomac Foundation, the multiplayer game allows users to take on the identities of different countries, complete with resources and political agendas.
Before you write it off as yet another game imitating life, consider this: Hegemon has quickly become a favorite with strategists and academicians who use the simulation to test different approaches and evaluate results.
Players can take on the roles of the United States, China and other countries in the Asia-Pacific region; from budgeting and strategizing to managing military and technological needs, the ‘game’ involves enacting real-world geopolitical relationships on-screen.
Perhaps the most interesting implication of the game is that it allows users to test the waters, so as to speak, on the South China Sea issue. And the revelations are rather edifying.
China could gain a hegemony on the South China Sea
As per an article first published in the Lowy Interpreter, China could gain and sustain a hegemony on the South China Sea without every actually having to resort to armed conflict. The South China Sea issue has been in the news frequently over the past year owing to a rise in hostile disputes over territory between the various claimants. China, most noticeably, has ‘reclaimed’ several territories and undertaken construction operations on the same, much to the chagrin of other stakeholders. As of this past month, the state has halted its actions in the region in keeping with an international effort to resolve the dispute peacefully. However, as the game has revealed, there are other ways in which the state could monopolize the region. Here are some possible outcomes to mull over.
#1 You Don’t Need To Fight A War To Win A War
A very big part of war strategy is avoiding war altogether. You must prepare to excel at the worst, but still keep it from happening at any cost. In the game, only 50% of the region takes to violence across a span of two decades. Instead, the more probable outcome is that countries turn to brokering agreements. It’s interesting to note that the matter of who plays the game affects what the outcome is: military personnel are more likely to opt for confrontational tactics while academics are more prone to choosing the non-combative options.
#2 The Role Of Russia
While Russia isn’t a claimant in the South China Sea issue, or even a regional stakeholder, the state does exert a considerable amount of influence on the area’s security and stability. Alliances and enmities with Russia can go a long way towards affecting the regional balance of power. History has proven that power in geopolitical conflicts is best consolidated through a formidable military presence in the region in question, and the fact that Russia is a significant contributor to the international weapons market all but guarantees Moscow a say-so in the South China Sea issue.
#3 What Would Vietnam Do?
Vietnam makes for a very interesting entry point into the South China Sea dispute because the state is a claimant in the territorial conflict and clearly opposed to Chinese monopoly in the greater South Asian region, but it still continues to be something of a wild card. The country has a land border in common with Beijing, so it serves Vietnam’s security interests to maintain peaceful ties with China. One probable outcome, as we see played out in Hegemon only too often, is that Hanoi is likely to forsake a portion of its stakes in the South China Sea issue in exchange for a decreased Chinese military presence at its borders.
#4 Diplomacy & Perseverance
Many real-world experts have argued that China will seek to avoid open confrontation simply because the costs of war are too high and the state has identified another means to the same end: diplomatic channels. China currently enjoys a position of enviable influence in the region. The current geopolitical landscape of South Asia is marked by an eagerness to either ally with China or, at the very least, avoid an armed conflict with the state. Analysts argue that by simply waiting it out China stands to gain more. As such, if China were to solidify its identity as the dominant regional power it would serve a severe blow to the United States’ ‘pivot to Asia’ strategy.
#5 Deterrence or Destruction?
Yet others argue that even if China were to persevere at the long game, there is no guarantee that other Asian states will concede to its hegemony in the region. China has a historical rival in Japan, and if things were to come to a head, the latter is most likely to align with the United States in an effort to maintain the status quo in Asia. In this case, the arms race and support gathering may result in a more pronounced divide than ever before, and scholars warn that the world might soon be looking at another iteration of the Cold War.
Interesting though it is to see how closely the game imitates real life and vice-versa, theorists will argue against basing actual strategy on gameplay simply because two crucial elements- the stakes involved and the time in hand- do not represent real-time situations accurately. Defeat in a game and defeat on a battlefield are two very different experiences indeed. And while overnight developments are not completely unheard of in military history, most issues develop gradually and decision-makers have months, even years, to chart the most preferred course of action.
So, while geostrategy buffs can definitely learn a thing or two about the South China Sea issue from Hegemon, and maybe even test-drive a few theories, the real world is, as they say, a totally different ballgame.

About the author
BRINDA BANERJEE
Brinda Banerjee is a researcher working on security, armed conflict and military policies. She holds a Bachelor’s in Journalism (with Honors), a Master’s in Peace and Conflict Studies and is currently pursuing her Ph.D. in state responses to internal conflict. Brinda writes extensively about current events, conflict resolution and geopolitical dynamics in the modern world.
Copyright © 2015 ValueWalk